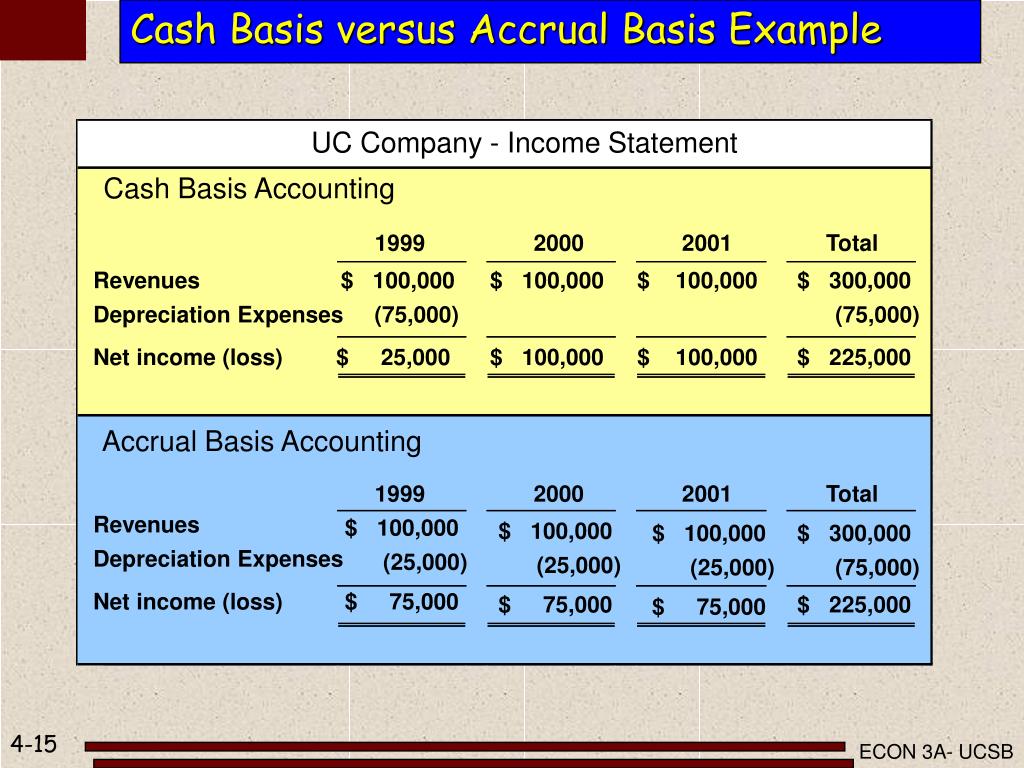
Cash Basis Accounting Balance Sheet Example. Cash-basis accounting is a primary method that small businesses use to keep track of their income and expenses. Nor can it—by itself—give owners and managers crucial information for evaluating the firm's. balance sheet. this shows the resources of a company, the company's obligations, and the equity of the owners at a certain point in time. accounting approach where the company records revenue only when it receives cash, records expenses only when it pays cash; GAAP prohibits cash-basis.

Cash basis accounting cannot meet the record-keeping needs of public companies and other organizations that must file audited financial statements, such as an Income statement or Balance sheet.
And just so you have some context, the cash basis is any time you.
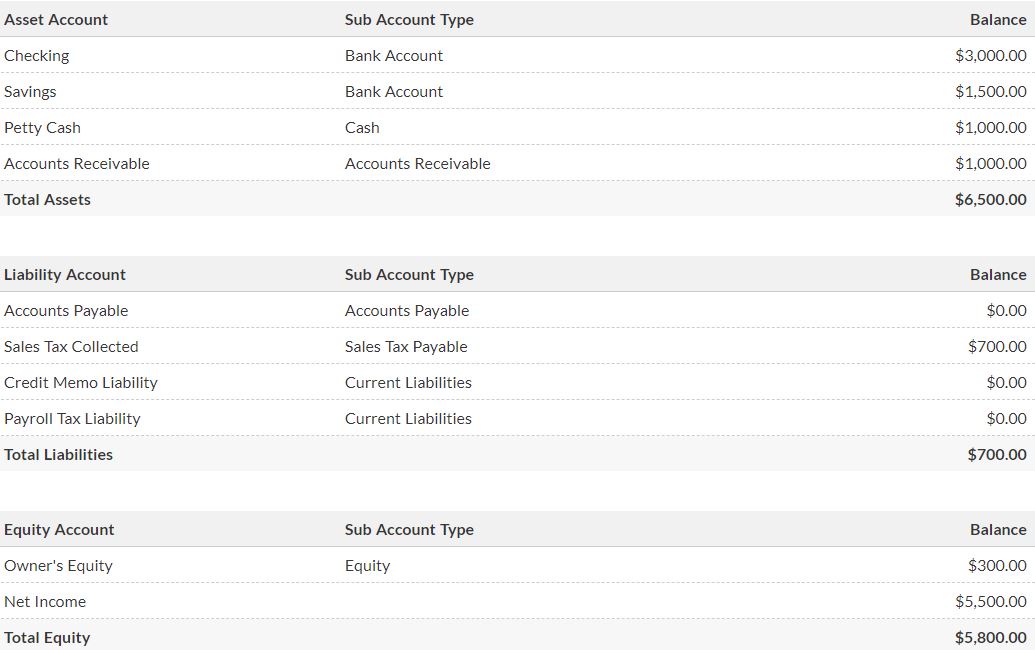
The Cash Basis Balance Sheet (CBBS) shouldn't show Accounts Receivable (A/R) or Accounts Payable (A/P) balances because these accounts track open (unpaid) invoices and unpaid bills. The classified balance sheet helps users of financial statements Part of the cash balance invested in the business that represented owner's equity was used for the asset land. Under cash basis accounting, revenue and expenses are recorded when cash is actually paid or received.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/women-preparing-taxes-135594732-57361deb3df78c6bb0480a83.jpg)